Camera techniques
Visual dictionary
Extreme close-up: An extreme close upshot is a shot that is often used to point out small detailed areas or subjects such as parts of the face, fruits, and animals.

Close-up: Close-ups are one of the most common shots usually used with medium and long shots. Close-ups are capturing the face and the emotions and the reactions they have on it.
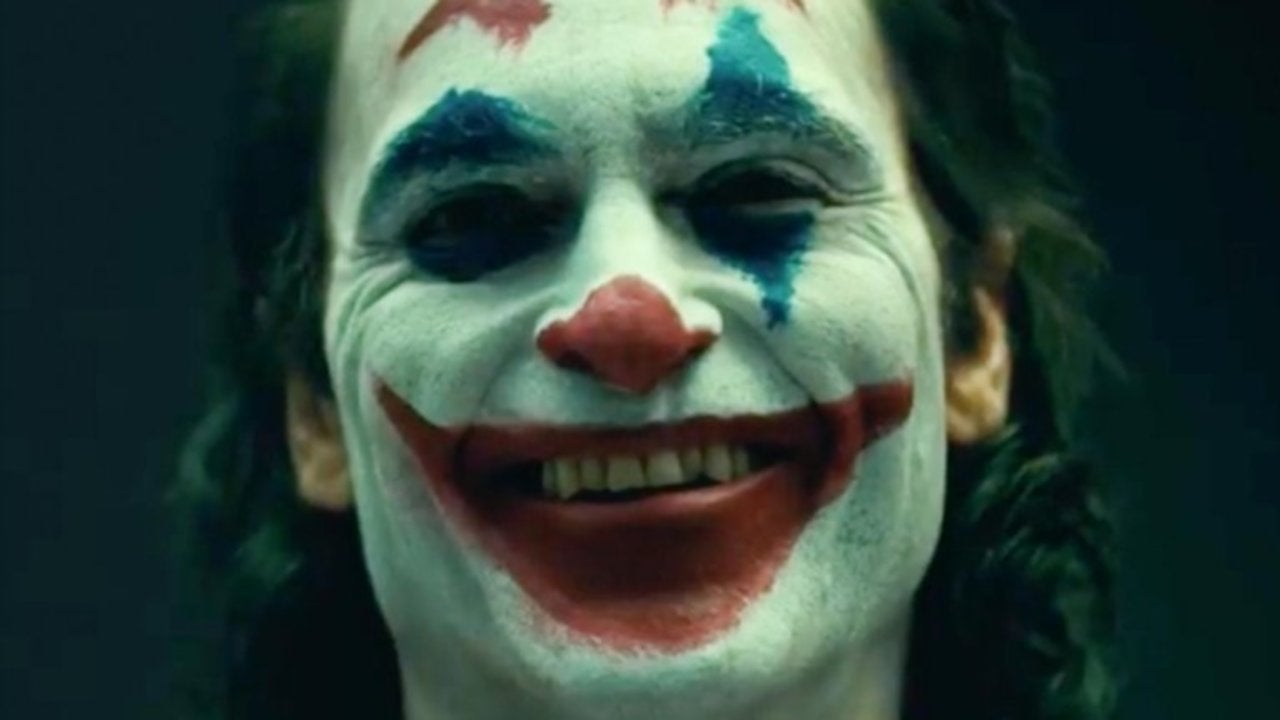

Medium close-up: Medium is a shot that is tightly framed of a person or subject from their chest or shoulders up. Mediums are used when there are “natural” scenes or with scenes showing full face emotions.
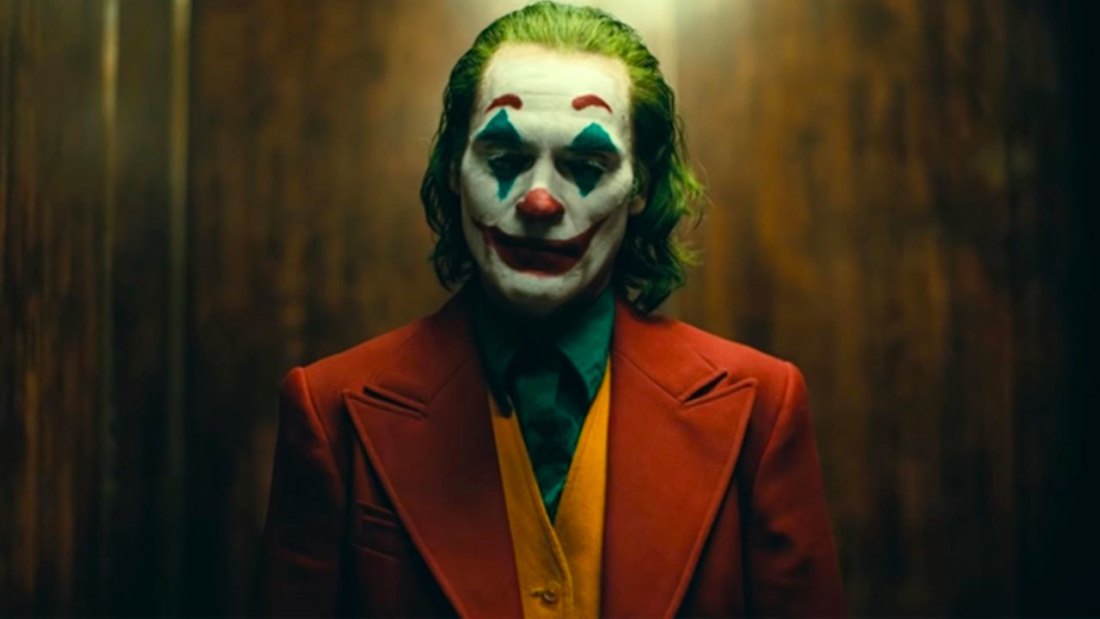

Medium shot: Medium shots are usually taken from the waist up, it catches more of the setting and the characters body language It is also used for dialogue scenes.

Medium long shot: A medium long shot is taken from the knees up it is generally used for group shots as the frame can include from many characters or visual elements simultaneously. The shot is in between a medium and a long shot making it able to see more of the setting and body language the character has.
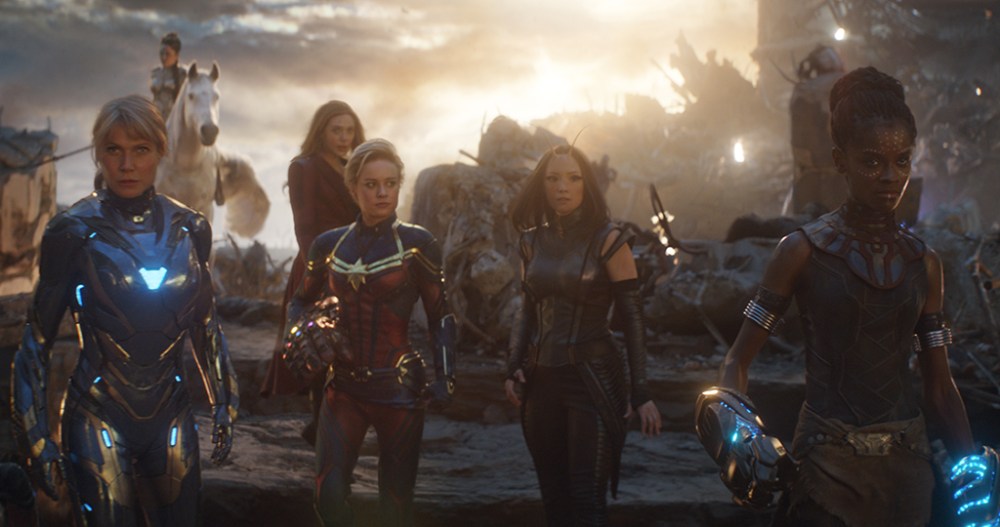
Long (wide) Shot: A wide shot is a shot usually taken of the whole person or object and is easily captured - A long shot is used to indicate a location around the subject.

Extreme Long-Shot: A extreme long shot is a shot from the distance showing the landscape making the human figure or an object look small.
![HQ] Extreme Long Shot Pictures | Download Free Images on Unsplash](https://lh4.googleusercontent.com/Xnux1ByL8ERWdSwiP5es4EAfyMeVTB2t_5STj_oc8_0TckK2lbOAKAUfMJFArr4du4-eM8w688cOasH_1GZcTSoDjulJpgewlvq6F5xbywW0FYeUcVC28dlVeY9kBE5CZ0remuel)
Low Angle: a low angle is a shot from which is taken low on a vertical angle from anywhere under the eye line to possibly below the feet of the subject, It is often used to make the subject feel powerful or threatening.
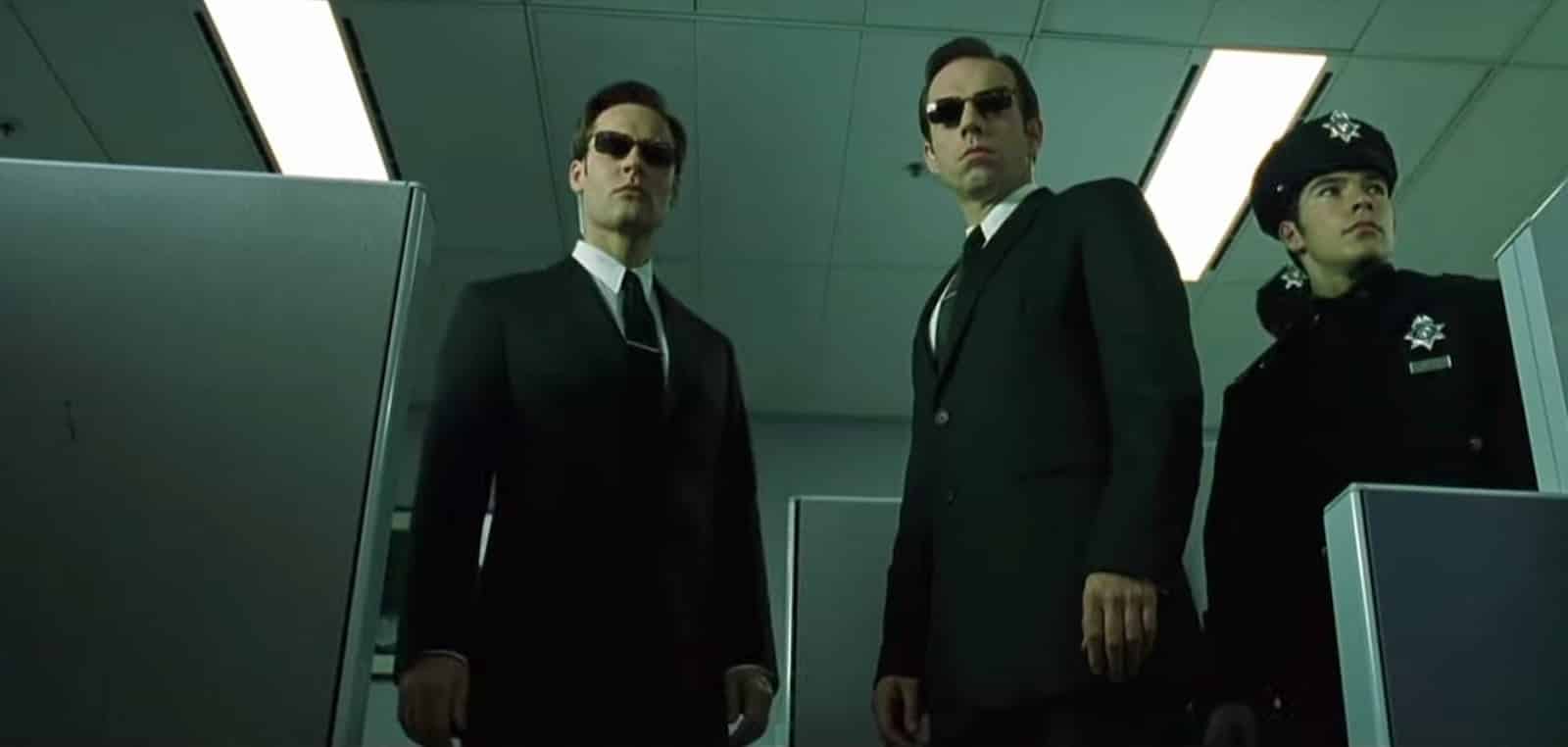

High Angle: The high angel shot is a technique where the camera is facing down at the subject from a high angle making the subject look weak or vulnerable.

Eye Level: An eye-level is the most common shot. It is a camera positioned so the subject can look into the camera without having to move their eyes up or down. It is considered to be emotionally neutral and is best used for straight, factual presentation

Birds Eye View: A birds-eye view is a view from a high angle as if seen by a bird in flight. It is a view that is seen as a bird might see it, from an elevated perspective.

Dutch Tilt: A Dutch tilt is a camera shot in which the camera angle is slanted to one side - this can be used for dramatic effect.

Pan: A pan shot or panning shot is a technique where you follow a moving subject, and you can shoot this with a slower shutter speed to create a feeling of speed or action

Tilt: A tilt shot is a shot that uses a cinematographic technique called tilting in which the camera stays fixed but rotates up and down on a vertical plane

Tracking: A tracking shot is any shot where the camera follows backward, forward, or moves alongside the subject being recorded.

Point of View: A point of view shot is a film angle that shows what a character is looking at in the first person.
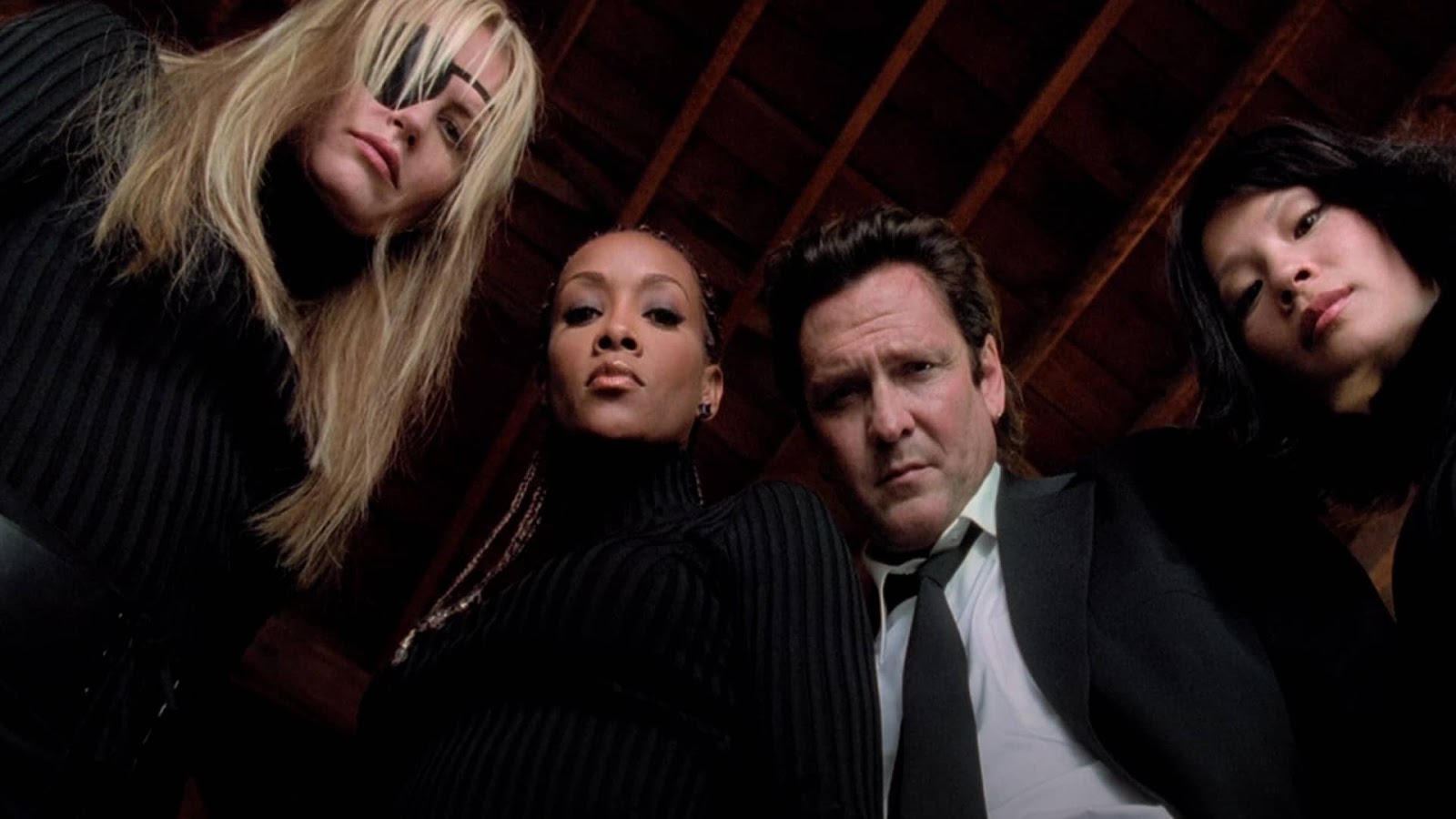

Over the shoulder: An over the shoulder shot is when the camera is positioned behind one character and facing another.
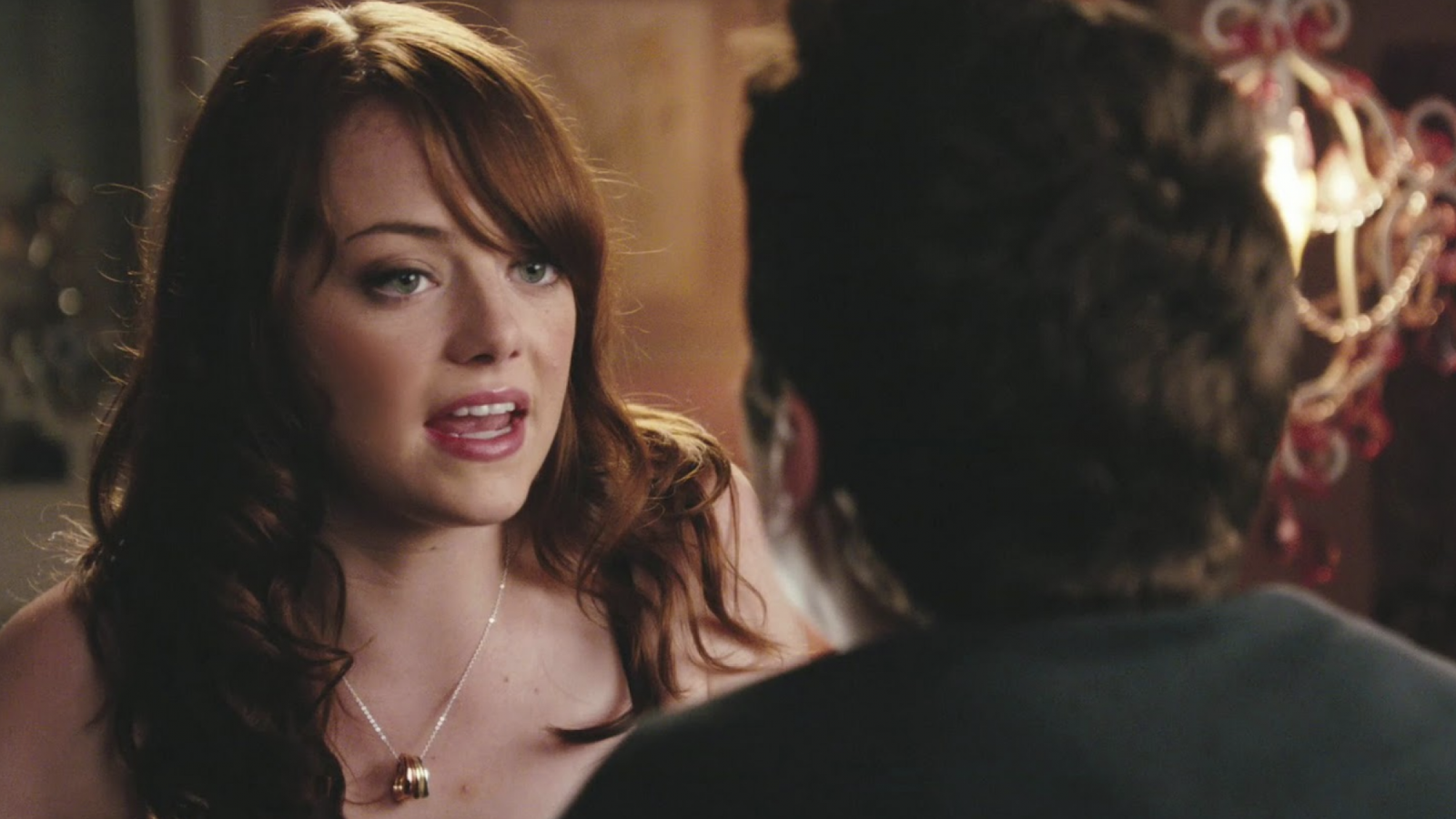

Mise En Scene: Mise en scene is the stage design and arrangement of actors in scenes for a theatre or film production, both in visual arts through storyboarding, visual theme.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
What am I learning?
I am learning to understand the different types of language used in film and Camera techniques.
How does this work show my learning?
To show that I know and understand what I’m learning about.
What am I wondering as a result of this learning?
I am wondering who made all of these techniques and angles.

